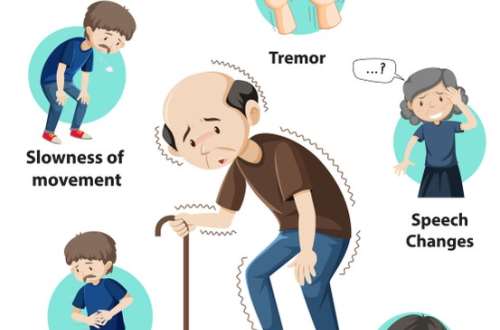
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the progressive loss of dopamine-producing cells in the brain. While the exact causes of PD remain elusive, several studies have suggested a potential link between exposure to pesticides and an increased risk of developing this debilitating condition. In this article, we delve into a recent groundbreaking study that has identified specific pesticides that could influence Parkinson’s disease.
Study identifies pesticides that could influence Parkinson’s disease
The Study
A team of researchers conducted an extensive analysis of existing literature and epidemiological studies to identify the pesticides that may be associated with an elevated risk of developing PD. Their findings, published in a reputable scientific journal, shed light on the potential role of certain pesticides in contributing to the onset and progression of Parkinson’s disease.
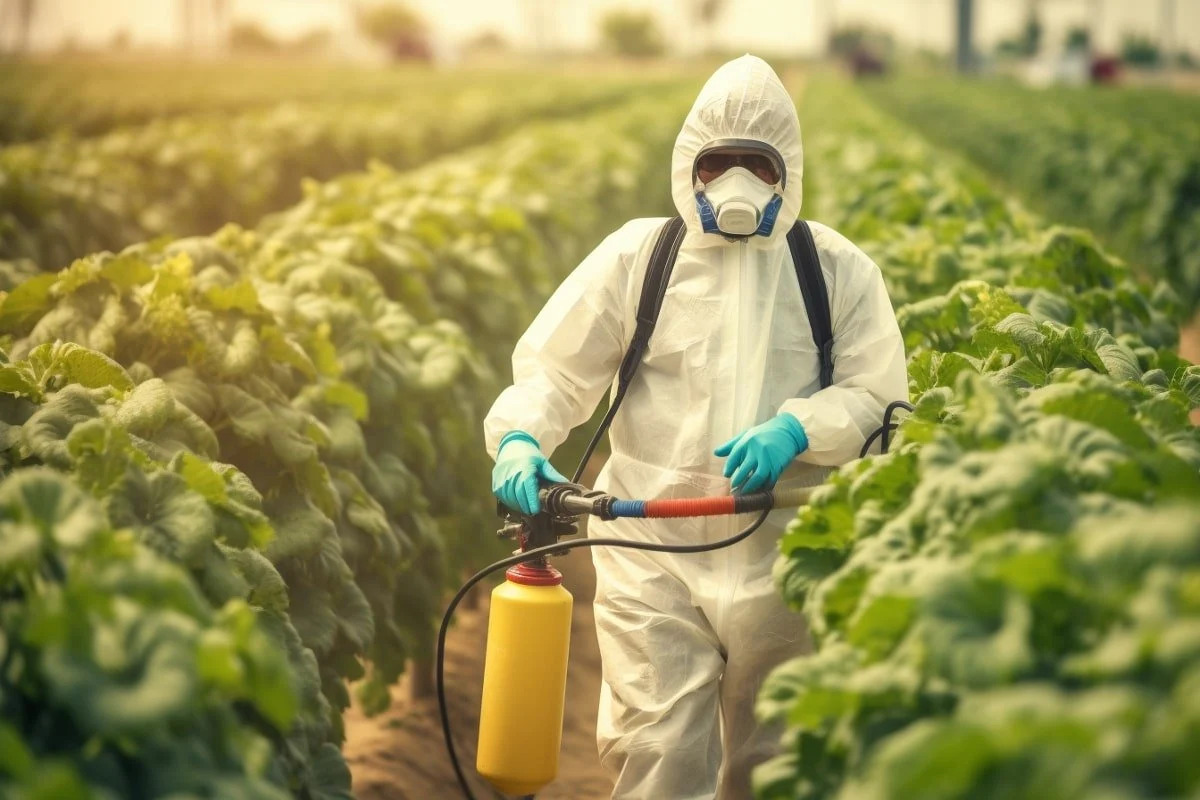

Pesticides and Dopamine
Dopamine, a neurotransmitter crucial for motor control and other vital brain functions, is significantly affected in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. The study explored how exposure to pesticides might disrupt dopamine regulation in the brain, providing insights into the mechanistic relationship between pesticide exposure and PD.
Identified Pesticides
The research identified several pesticides that showed a consistent association with an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease. Among these were organochlorine insecticides, such as DDT and dieldrin, and herbicides like paraquat and maneb. These pesticides are commonly used in agriculture and have been found to accumulate in the environment and food chain.
Mechanisms of Action
The study delved into the potential mechanisms through which these pesticides may influence the development and progression of Parkinson’s disease. The researchers highlighted the ability of certain pesticides to interfere with cellular pathways involved in oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and protein aggregation—all of which are key factors implicated in PD pathology.
Epidemiological Evidence
The research team also reviewed numerous epidemiological studies that supported the association between pesticide exposure and Parkinson’s disease. They observed that individuals occupationally exposed to these identified pesticides, such as farmers and agricultural workers, exhibited a higher prevalence of PD compared to the general population. These findings strengthen the hypothesis that pesticides play a significant role in the etiology of Parkinson’s disease.
Implications and Future Directions
The identification of specific pesticides linked to Parkinson’s disease has substantial implications for public health and regulatory policies. The study highlights the need for stricter regulations and better monitoring of pesticide use, particularly in agricultural settings, to minimize the risk of PD development.
Furthermore, this research emphasizes the importance of continued investigation into alternative methods of pest control that are less reliant on potentially harmful chemicals. Developing sustainable and eco-friendly approaches to agriculture could help reduce the widespread exposure to pesticides and, subsequently, the incidence of Parkinson’s disease.
Conclusion
The study provides compelling evidence linking certain pesticides to an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease. By identifying the specific pesticides that may influence the onset and progression of PD, this research contributes to a better understanding of the disease’s etiology. Moving forward, it is crucial to implement stricter regulations, enhance public awareness, and promote safer alternatives to pesticide use to protect individuals from the potential hazards associated with these chemicals. Ultimately, this knowledge brings us one step closer to preventing and managing Parkinson’s disease effectively.
Must Read: Daily Habits That Boost Your Positive Mental Health
Senolysis holds great promise for developing new therapeutics for cancers and age-related diseases
7 Tea Leaf Recipes To Bring Its Health Benefits To Your Plate
Spicing Up Your Workout Routine: Medicine Ball Exercises at Starbucks
6 Major Health Benefits of Consuming Honey-Coated Dried Fruits









Leave a Reply